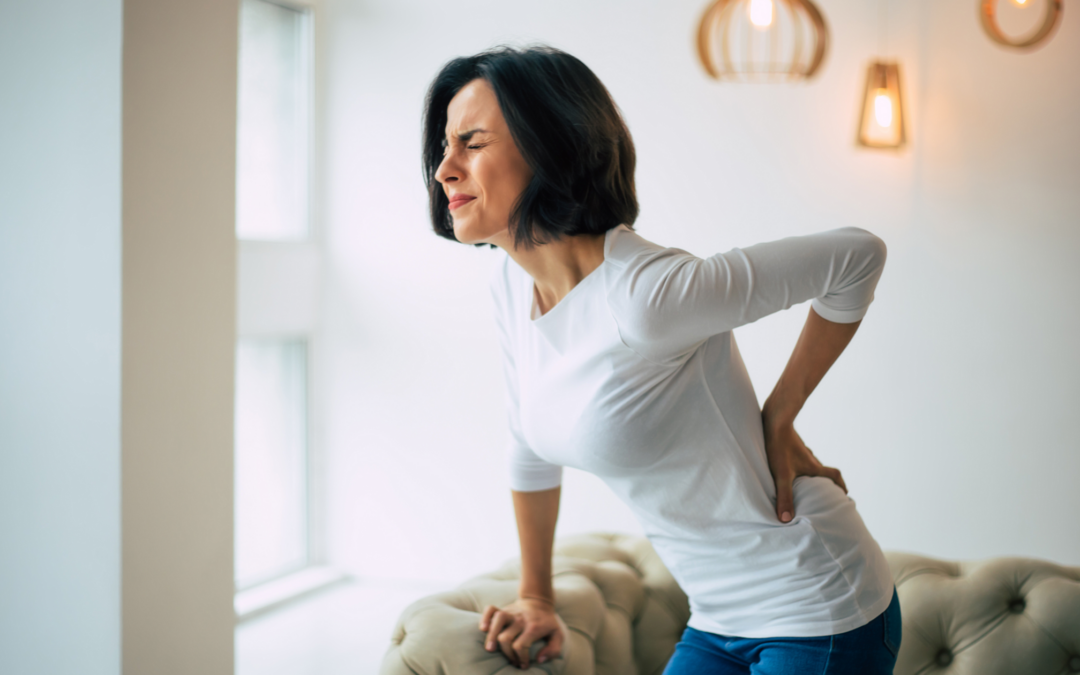

The Most Common Causes of Chronic Back Pain
Chronic back pain affects millions of people worldwide, disrupting daily routines and diminishing the quality of life. It’s often linked to various factors, from lifestyle habits to underlying medical conditions. While occasional discomfort may be manageable, persistent back distress can signal a deeper issue requiring attention. Understanding the potential causes and available treatments is a key step in addressing this common problem.
Causes of Chronic Back Pain
Chronic back pain stems from a variety of sources, many of which develop gradually over time. Repetitious movements, particularly in physically demanding jobs or repetitive tasks, often place continuous strain on the back muscles. These repetitive actions eventually lead to overuse and muscle fatigue, which may trigger lingering discomfort.
Sudden trauma is another leading cause of back pain. Injuries from accidents, falls, or sports can damage muscles, ligaments, or the backbone itself. These incidents may result in strains or more severe structural problems, such as herniated discs or fractures, that can deeply affect mobility and create long-lasting pain.
Structural degeneration in the spine is also a prevalent factor for developing chronic back discomfort. Degenerative conditions include facet joint arthritis, degenerative disc disease, spinal stenosis, and bone spurs, all of which limit flexibility and can inflame surrounding tissue. Vertebral compression fractures and slipped vertebrae (spondylolisthesis) further complicate mobility while amplifying discomfort.
These causes often overlap, making it more challenging to identify the root problem without professional evaluation. Persistent back discomfort, particularly when tied to structural issues, frequently requires medical support to minimize its effects.
Treatments for Back Pain
Managing chronic back pain starts with understanding its root cause, which can open the door to various treatment options aimed at improving comfort and mobility. These approaches range from non-invasive methods to more advanced medical procedures, depending on individual needs.
Non-invasive techniques like massage or acupuncture can help relax muscles and promote circulation, while physical therapy exercises often focus on strengthening the back and core to enhance overall support. Behavioral approaches, such as therapy, may also complement physical treatments to support long-term pain management.
For some, injection-based treatments might be an option. These can include injections aimed at reducing inflammation or addressing specific areas of discomfort in muscles or joints. These methods are often tailored to the individual’s pain source to provide targeted relief.
In cases involving structural issues, surgical solutions may be used. Minimally invasive techniques aim to address problems like herniated discs or spine stability while reducing recovery times.
Innovative therapies are also emerging, offering new possibilities for individuals with persistent pain. While these approaches are still developing, they explore alternative ways to manage discomfort and provide new options for those seeking relief.
Take the First Step Toward Relief
Chronic back pain can feel overwhelming, but numerous treatments are available to help manage and improve your condition. Whether your pain stems from a physical injury, repetitive strain, or spinal degeneration, professional evaluation can guide you toward the most effective solutions. Don’t wait—seeking support from qualified specialists can set you on the path to relief and better quality of life.
You May Also Like

Anheihe – The Ultimate Guide!
May 13, 2024
Google’s 25e Verjaardag – AgUide By Industry Expert!
April 5, 2024

Average Rating