Public Cloud vs Private Cloud: Pros and Cons Unveiled
Businesses increasingly rely on cloud computing to enhance operations, improve scalability, and reduce costs. With various cloud options, companies often debate which cloud service best suits their needs. Among the most common choices are public and private cloud solutions, each offering distinct advantages and potential drawbacks.
Understanding the nuances of public cloud vs private cloud is essential for making an informed decision that aligns with your organisation’s goals and requirements. This page will explore the pros and cons of both models, helping you determine the best fit for your business.
Cost Considerations
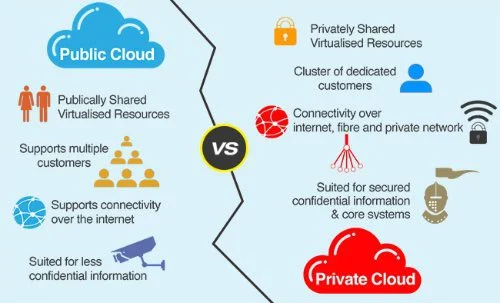
One of the primary factors that businesses consider when choosing between public and private clouds is cost. Public cloud services are typically more cost-effective because they operate on a shared infrastructure model. They often offer a pay-as-you-go pricing model, which can be very attractive for businesses with fluctuating workloads.
On the other hand, private solutions involve dedicated hardware and resources for a single organisation. They are generally more expensive to implement and manage, making them a better fit for organisations with stable workloads and specific security or compliance requirements.
Scalability and Flexibility
Scalability is another crucial factor in this debate. Public cloud services are renowned for their high scalability and flexibility. Businesses can quickly scale resources up or down based on their needs, allowing for quick adaptation to changing demands. This elasticity makes them ideal for organisations experiencing rapid growth or seasonal variations in workload.
Scaling a private involves purchasing and installing additional hardware, which can be time-consuming and costly. However, private provide more environmental control, enabling organisations to customise their infrastructure to meet specific requirements.
Security and Compliance
Security is a top concern for many businesses when selecting a model. Private solutions offer higher security because they are dedicated to a single organisation. This isolation reduces the risk of data breaches and allows for greater control over security measures. Private are often preferred for industries with stringent regulatory requirements, such as healthcare and finance.
While generally secure, the public operates on a shared infrastructure, which can raise concerns about data privacy and security. However, reputable providers invest heavily in security measures and comply with industry standards to protect their clients’ data.
Performance and Reliability
Public cloud providers typically offer high levels of reliability and performance, supported by extensive infrastructure and redundant systems. Businesses benefit from the provider’s robust network, data centres, and expertise, ensuring minimal downtime and fast resource access.
Private also delivers strong performance and reliability, often tailored to the organisation’s needs. Since the resources are not shared, businesses can optimise their environment for maximum efficiency. However, the reliability depends on the organisation’s ability to maintain and manage the infrastructure effectively.
Management and Maintenance
Public services offer significant advantages in terms of management and maintenance. The provider handles all aspects of infrastructure management, including updates, security patches, and hardware maintenance.
In contrast, private solutions require the organisation to manage and maintain the infrastructure. This includes handling updates, security, and performance monitoring. While this provides greater control, it also demands more resources and expertise. Businesses must weigh the benefits of control against the potential burden of managing the environment.
When evaluating public cloud vs private cloud, it’s essential to consider factors such as cost, scalability, security, performance, and management requirements. Public offers cost efficiency, scalability, and ease of management, making them ideal for businesses with dynamic workloads and limited IT resources. Private provides enhanced security, control, and customisation, suitable for organisations with specific regulatory needs and stable workloads. Ultimately, the choice depends on your organisation’s unique needs and priorities, ensuring you select the cloud model that best supports your business objectives.
You May Also Like

The Artistic Trailblazer: A Comprehensive Dive into u/jackerman3d’s Reddit Journey
March 11, 2024
GoCryptoBet.com Walletv- Secure Crypto Transactions!
February 13, 2025


Average Rating